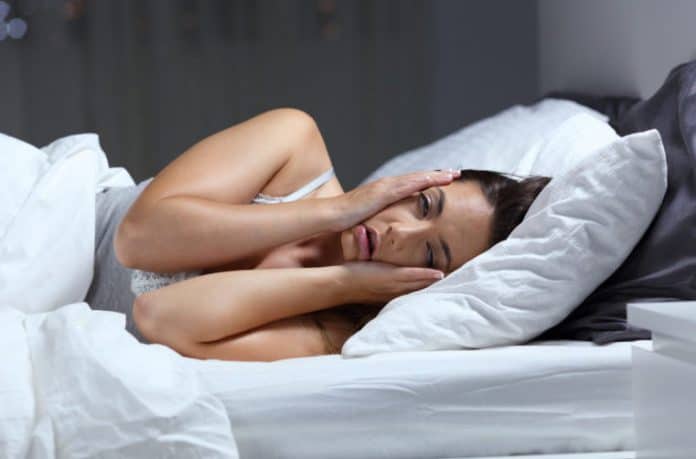
A tired day calls for a good indoor breathing night’s sleep. However, sleeping in the comfort of your cozy bed sounds too tempting.
Does the bed, warm quilt, and fluffy pillow put you down for deep sleep?
The air we breathe indoors is often rife with pollutants, ranging from dust and pet dander to volatile organic compounds (VOCs) emitted by household cleaners, paints, and furnishings. Additionally, inadequate ventilation exacerbates the problem by trapping these contaminants indoors, creating a cocktail of potentially harmful substances that we inhale night after night.
So, how does this compromised air quality impact our sleep?
Firstly, pollutants can irritate the respiratory system, triggering symptoms such as coughing, sneezing, and congestion, all of which can disrupt sleep or prevent us from reaching deep sleep stages. Furthermore, exposure to airborne allergens like dust mites can exacerbate conditions such as asthma, leading to further sleep disturbances and compromising overall sleep quality.
Moreover, certain pollutants, such as VOCs, have been linked to adverse health effects ranging from headaches and dizziness to more serious conditions like respiratory and cardiovascular diseases. These health implications not only affect our ability to sleep soundly but also undermine the body’s ability to fully recover during rest.
The importance of addressing indoor air quality extends beyond ensuring a good night’s sleep. It encompasses safeguarding our long-term health and well-being. Fortunately, there are steps we can take to mitigate indoor air pollution and promote better sleep hygiene.
Investing in high-quality air purifiers equipped with HEPA filters can help remove a significant portion of airborne contaminants, creating a cleaner and healthier indoor environment conducive to restful sleep. Additionally, regular maintenance of HVAC systems and proper ventilation can improve air circulation and reduce the buildup of pollutants indoors.
For a healthy adult, 13-23% of the sleep is deep sleep, roughly 60-110 minutes per 8 hours. With the drop in the air quality, can you have a calming indoor breathing sleep that helps your body recover?
The answer is no. Unless you live a lonely life at the peak of a mountain all by yourself, you can be assured that your body is not recovering as well as it should from bad indoor breathing air.
Table of Contents
Can Indoor Breathing Air Quality Affect Sleep?
The indoor breathing air quality has a direct impact on your sleep. Many people boast of sleeping in the nosiest or well-lit rooms without drawing their curtains, but none can boast of having a quality sleep with poor air quality.
Poor indoor breathing air quality inside your home can impact not just your sleep but overall health as well. The rising pollution level outdoors has been the talk of many developed countries for years. But unfortunately, this has further degraded the air within the homes.
In recent years, there has been increasing concern about outdoor air pollution in many developed countries. However, the air quality inside our homes can be equally, if not more, concerning. Indoor air pollutants such as dust, pet dander, pollen, mold spores, and volatile organic compounds (VOCs) can accumulate and linger in our living spaces, compromising the air we breathe, especially during the night when windows are often closed.
The relationship between indoor air quality and sleep is complex but significant. Here are some ways poor indoor air quality can affect your sleep:
- Respiratory Issues: Airborne particles and pollutants can irritate the respiratory system, leading to congestion, coughing, sneezing, and difficulty breathing. These symptoms can make it harder to fall asleep and stay asleep throughout the night.
- Allergies and Asthma: For individuals with allergies or asthma, poor indoor air quality can exacerbate symptoms, triggering allergic reactions or asthma attacks. Wheezing, chest tightness, and shortness of breath can disrupt sleep and lead to daytime fatigue.
- Discomfort: High humidity levels or stuffy indoor environments can cause discomfort and make it harder to get comfortable enough to fall asleep. Conversely, excessively dry air can lead to irritated nasal passages and throat, exacerbating snoring and sleep disturbances.
- Chemical Exposure: VOCs emitted from household products such as cleaning supplies, paints, and furnishings can contribute to indoor air pollution. Prolonged exposure to these chemicals, especially in poorly ventilated spaces, may have adverse health effects and disrupt sleep patterns.
- Temperature Regulation: Indoor air quality is closely linked to temperature and humidity levels. Extreme temperatures or fluctuations can disrupt the body’s ability to regulate its internal temperature, leading to sleep disturbances and discomfort.
Improving indoor air quality can have a positive impact on sleep and overall health. Here are some steps you can take to enhance the air quality in your home:
- Ventilation: Proper ventilation is crucial for circulating fresh air and reducing indoor pollutants. Open windows when weather permits, use exhaust fans in kitchens and bathrooms, and consider installing an air purifier with a HEPA filter to remove airborne contaminants.
- Reduce Sources of Pollution: Identify and minimize sources of indoor air pollution, such as smoking, burning candles or incense, using harsh cleaning products, and storing chemicals indoors. Opt for natural cleaning alternatives and choose low-VOC or VOC-free products whenever possible.
- Maintain Cleanliness: Regular cleaning and dusting can help reduce the accumulation of dust, pet dander, and other allergens in your home. Wash bedding and curtains frequently, vacuum carpets and upholstery, and keep pets groomed to minimize shedding.
- Monitor Humidity Levels: Maintain indoor humidity levels between 30% and 50% to prevent mold growth and respiratory issues. Use a hygrometer to monitor humidity levels and use a dehumidifier or humidifier as needed to achieve optimal comfort.
- Choose Sleep-Friendly Materials: Opt for hypoallergenic bedding and mattress materials to reduce exposure to allergens. Avoid synthetic fragrances and opt for natural, organic materials in furnishings and household products.
How Does Air Quality Impact Sleep?
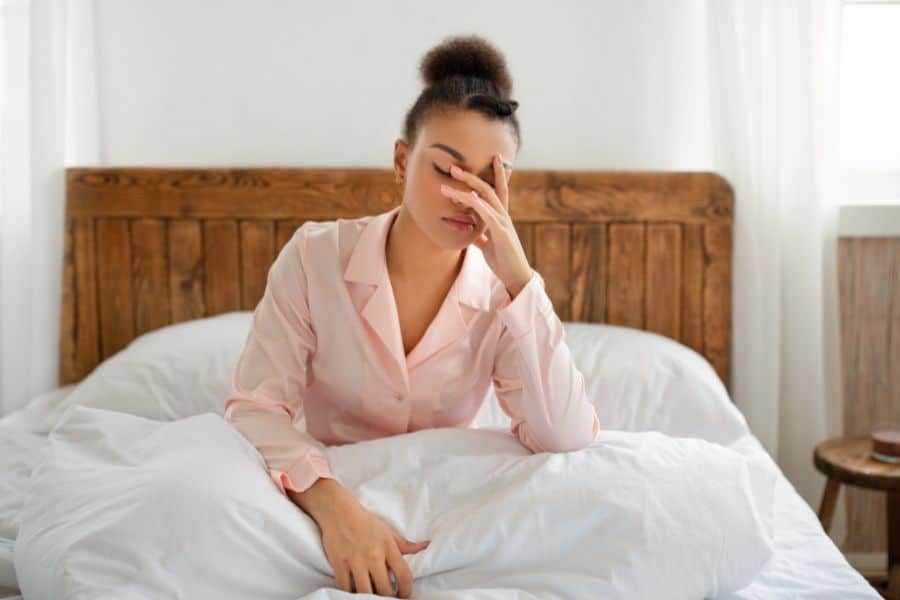

Air quality impacts the breathing pattern and alleviates allergy symptoms. A few common factors that affect the air quality are the allergens like pet dander, dust, and dust mites in the beds.
These things can interrupt deep sleep and cause breathing issues that will not let the body rest and recover appropriately.
Humidity in the air also has a huge impact on sleep. Too much or too little moisture indoors can significantly determine your sleep quality.
Too humid rooms will increase the indoor temperature and warm the room, while dry air can cause dry nasal passages and itchy skin. Both of these is not ideal situation to rest in.
A good night’s sleep is crucial for overall health and well-being, yet many factors can disrupt this essential nightly ritual. Among these, air quality plays a significant role, influencing breathing patterns and exacerbating allergy symptoms. Understanding the relationship between air quality and sleep can shed light on how to optimize our sleep environments for better rest.
Allergens and Sleep Interruption
Common allergens like pet dander, dust, and dust mites often lurk in our indoor environments, including our beds. These microscopic particles can infiltrate bedding, carpets, and upholstery, triggering allergic reactions and respiratory issues. For individuals sensitive to these allergens, exposure during sleep can lead to disruptions in breathing patterns, causing snoring, congestion, or even sleep apnea. Consequently, deep sleep becomes elusive, and the body’s ability to rest and recover is compromised.
Humidity’s Role in Sleep Quality
Humidity levels in the air also significantly impact sleep quality. An imbalance in moisture content—whether too high or too low—can disrupt the body’s natural sleep mechanisms.
Excess Humidity: Rooms with high humidity levels can feel stifling, as moisture-laden air traps heat and raises indoor temperatures. This uncomfortable environment can hinder the body’s ability to regulate its temperature, leading to restless sleep and frequent awakenings. Moreover, high humidity fosters the growth of mold and mildew, further exacerbating respiratory issues and allergy symptoms.
Insufficient Humidity: Conversely, dry air poses its own set of challenges to sleep quality. Low humidity levels can parch nasal passages, throat, and skin, causing irritation and discomfort. Dry air can also exacerbate conditions like asthma and eczema, leading to nighttime itching and inflammation that disrupt sleep. Additionally, dry air can increase static electricity, leading to discomfort from shocks and further disrupting restful sleep.
Why Is Indoor Air Quality Worse At Night?
The polluting factors outside the house do not just determine air quality. Various daily activities in the house can also cause air quality to drop.
For example, tobacco smoke, car exhaust, and oil/gas can impact indoor air quality. So, while one may think that the pollution at night drops and the air quality should improve, it is the opposite.
This is because as the temperature drops, CO2 emissions, car emissions, and various other pollutants start getting trapped in the atmosphere.
If the house is not adequately ventilated, the trapped pollutants stay within your home and affect the quality of your sleep.
The Multifaceted Nature of Indoor Air Quality: Indoor air quality is not solely determined by external factors such as industrial emissions or vehicular exhaust. Indeed, everyday activities within the confines of our homes can also contribute to a decline in air quality. Whether it’s the lingering remnants of tobacco smoke, the fumes from cooking with oil or gas, or the allergens brought in from the outside, various pollutants can infiltrate our indoor environment.
The Temperature Factor: One might assume that as night falls and temperatures drop, outdoor pollutants dissipate, leading to an improvement in indoor air quality. However, the reality is quite the opposite. As temperatures decrease, pollutants such as carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions and vehicle exhaust have a propensity to linger in the atmosphere. Without adequate ventilation, these pollutants find their way into our homes, where they accumulate and pose a threat to our health.
Stagnation and Trapped Pollutants: Another crucial aspect contributing to the deterioration of indoor air quality at night is the lack of ventilation. During the day, windows and doors are often left open, allowing for natural airflow and the dispersion of pollutants. However, as night falls, these openings are typically closed for security and energy conservation purposes. Consequently, indoor air becomes stagnant, providing a conducive environment for pollutants to accumulate.
Impact on Sleep Quality: The repercussions of poor indoor air quality extend beyond physical health; they also affect our sleep quality. The presence of pollutants such as dust mites, pet dander, and mold spores can exacerbate allergies and respiratory issues, leading to disrupted sleep patterns and decreased overall well-being.
Mitigating Measures: Despite the challenges posed by worsening indoor air quality at night, there are several steps individuals can take to mitigate its effects. Ensuring adequate ventilation by opening windows or using mechanical ventilation systems can facilitate the exchange of indoor and outdoor air, reducing pollutant buildup. Additionally, incorporating air purifiers equipped with HEPA filters can help capture and remove airborne contaminants, thereby improving indoor air quality.
How Can Pollutants Impact Sleep Quality?

A bedroom with a comfortable temperature and a slight breeze from a window or fan is ideal for sleeping.
A stuffed room with no ventilation isn’t a place to recover. The warmer a room gets, it makes you feel uncomfortable.
If all windows and doors of the room are shut, the CO2 exhaled is trapped in the same room while one is sleeping. As a result, it can lead to a rise in CO2 levels, three times more than recommended.
Overnight exposure to CO2 leads to low sleep efficiency, further impacting the next day’s smooth cognitive function.
Optimal sleeping conditions involve a bedroom with comfortable temperature settings and adequate ventilation. A slight breeze from an open window or a fan can promote air circulation, creating a conducive environment for rest. Conversely, a stuffy room devoid of ventilation becomes a breeding ground for pollutants, making it challenging to achieve quality sleep.
One of the primary pollutants that can accumulate in an enclosed sleeping space is carbon dioxide. When windows and doors remain shut, the CO2 exhaled by occupants gets trapped within the room, leading to a gradual buildup of this gas. Studies indicate that CO2 levels in bedrooms can reach concentrations up to three times higher than the recommended levels for indoor air quality.
The consequences of overnight exposure to elevated CO2 levels extend beyond mere discomfort. Research has shown that high concentrations of CO2 can compromise sleep efficiency, disrupting the normal sleep cycle and reducing the overall quality of rest. As a result, individuals may experience fragmented sleep patterns, frequent awakenings, and a decreased duration of deep, restorative sleep stages.
The impact of pollutants on sleep quality goes beyond the immediate physiological effects. Poor sleep resulting from exposure to indoor pollutants can have significant repercussions on cognitive function and daytime performance. Sleep is essential for consolidating memories, processing information, and maintaining optimal brain function. When sleep quality is compromised due to environmental factors like CO2 buildup, individuals may experience difficulties with concentration, memory recall, and problem-solving abilities during the day.
Can Particle Pollution Disrupt Sleep?

Particle pollution, called PM2.5, is tiny droplets or particles in the air that are small enough to enter your body through the nose and reach the lungs.
These particles have a width of 2.5microns and are considered more dangerous than larger pollution particles. These cause harm to the lungs and can also enter the bloodstream.
Common symptoms include coughing, runny nose, sneezing, and breathing problems. In addition, too much exposure to PM2.5 can cause restless or disrupted sleep. Sleeplessness is also considered an effect of particle pollutant exposure.
Air pollution also causes a sleeping disorder called “Sleep apnea.” With this disorder, one’s breathing is impacted while sleeping.
The breathing stops and continuously starts while sleeping, thus impacting an uninterrupted sleep. This leads to fatigue during the day, irritability, and drowsiness in the long term.
PM2.5, the microscopic particles suspended in the air, measuring a mere 2.5 microns in width, might seem inconsequential at first glance. Yet, these minuscule particles possess a menacing potency. Able to penetrate deep into our respiratory system upon inhalation, they pose a grave threat to our health.
The adverse health effects of PM2.5 are well-documented. From respiratory issues like coughing, wheezing, and shortness of breath to more severe conditions such as asthma and cardiovascular diseases, the toll on our physical well-being is significant. However, the pernicious reach of particle pollution extends beyond the realm of the respiratory system.
Recent studies have shed light on the potential link between PM2.5 exposure and disrupted sleep patterns. It’s not merely the discomfort of a runny nose or a persistent cough that disturbs our slumber; rather, it’s the intricate interplay between these airborne pollutants and our body’s internal rhythms.
One of the primary mechanisms through which particle pollution disrupts sleep is through its impact on the respiratory system. As these tiny particles infiltrate our airways, they trigger inflammation and irritation, leading to coughing fits and breathing difficulties, particularly during the night. This can result in fragmented sleep, with individuals waking up multiple times throughout the night, unable to achieve the restorative rest they desperately need.
Moreover, PM2.5 exposure has been associated with an increased risk of sleep disorders, notably sleep apnea. Characterized by interrupted breathing patterns during sleep, sleep apnea not only compromises the quality of sleep but also poses serious health risks. The recurrent pauses in breathing deprive the body of oxygen, leading to daytime fatigue, irritability, and in the long term, exacerbating the risk of cardiovascular problems.
What Can You Do To Increase Indoor Air Quality While You Sleep?
As mentioned before, ventilation is one of the best options to improve the air quality for sleeping.
Continuous in and out of the air will improve the air quality while sleeping. A running fan or an open window will also help check the CO2 levels inside.
However, this may not be a better solution if the pollution outside is higher. In such a case, opening the room’s doors to ensure airflow between rooms is a better option.
However, an air purifier is the best bet in such a scenario. Having an air purifier right where you sleep will give you clean air and decrease exposure to all night-time air pollution particles.
Quality sleep is crucial for overall well-being, and often, we overlook the significance of the environment we sleep in. One key aspect that can significantly impact the quality of our sleep is indoor air quality (IAQ). Poor IAQ can lead to discomfort, allergies, and even health issues in the long run. So, what can you do to enhance indoor air quality while you sleep? Let’s delve into some practical tips.
- Ventilation Matters: Adequate ventilation is fundamental for maintaining good IAQ. While sleeping, ensure there’s a continuous flow of fresh air. Opening windows, running fans, or using exhaust systems can facilitate this airflow. The exchange of indoor and outdoor air helps dilute indoor pollutants, including carbon dioxide (CO2), and replenishes oxygen levels.
- Consider Outdoor Pollution Levels: While opening windows or using fans for ventilation is generally beneficial, it’s essential to consider outdoor air quality. If outdoor pollution levels are high, bringing in outdoor air may introduce harmful pollutants indoors. In such cases, relying solely on natural ventilation may not be the best option. Instead, consider other strategies to improve IAQ.
- Utilize Cross-Ventilation: If outdoor air quality is a concern, employing cross-ventilation within your home can be effective. Keep interior doors open to allow air to flow freely between rooms. This promotes air circulation and prevents stagnation, reducing the buildup of indoor pollutants.
- Invest in an Air Purifier: An air purifier can be a game-changer for enhancing IAQ, especially during sleep. These devices work by filtering out airborne pollutants, including dust, allergens, and volatile organic compounds (VOCs). Place an air purifier in your bedroom to ensure that you breathe clean air throughout the night. Look for purifiers with HEPA filters, which are highly effective at capturing fine particles.
- Maintain Cleanliness: Regular cleaning of your sleeping environment can also contribute to better IAQ. Dust surfaces, vacuum carpets and upholstery, and wash bedding frequently to minimize the accumulation of dust mites, pet dander, and other allergens. Additionally, reduce clutter, as it can trap dust and impede airflow.
- Monitor Humidity Levels: Proper humidity levels are essential for IAQ. Aim for a relative humidity between 30% and 50% to prevent mold growth and maintain comfort. Use a hygrometer to monitor humidity levels and use a humidifier or dehumidifier as needed to achieve optimal conditions.
- Eliminate Indoor Pollution Sources: Identify and eliminate or minimize sources of indoor pollution. This includes smoking indoors, using harsh cleaning chemicals, and burning candles or incense, all of which can release harmful pollutants into the air. Opt for natural cleaning products and fragrance-free alternatives to reduce indoor air contaminants.
- Create a Green Oasis: Incorporating indoor plants into your bedroom can help improve IAQ by naturally filtering air pollutants and increasing oxygen levels. Choose plants known for their air-purifying properties, such as spider plants, peace lilies, or snake plants, to enhance your sleep environment.
Final Word
You can ensure a good night’s sleep by regularly cleaning the bedding, following standard hygiene practices, removing clutter from the room, and keeping dust and allergens out of the bedroom.
Since the bedroom is the most-used place in the house as one spends close to half the day, it is essential to keep the room clean.
Maintaining an excellent indoor air quality index is not as difficult as it may seem. It is also essential when one aims to have a quality sleep cycle daily.
Improving the air quality while you sleep will ensure you wake up refreshed and rested every day and give you a healthy life ahead.
Following standard hygiene practices extends beyond just cleaning the bedding. Personal hygiene, such as showering before bed and wearing clean sleepwear, helps remove dirt, oils, and bacteria from the skin, preventing them from transferring onto bedding and causing irritation. Moreover, practicing good oral hygiene, such as brushing and flossing before bedtime, reduces the risk of dental issues that can disrupt sleep and affect overall health.
Removing clutter from the bedroom is another essential step in creating a conducive sleep environment. A cluttered room can lead to feelings of stress and anxiety, making it difficult to relax and unwind before bedtime. By keeping surfaces clear and organizing belongings, you can promote a sense of calm and tranquility in the bedroom, allowing for better sleep quality.
Maintaining indoor air quality is crucial for a restful night’s sleep. Dust, allergens, and pollutants in the air can trigger allergies and respiratory issues, leading to discomfort and sleep disturbances. To improve indoor air quality, consider using air purifiers with HEPA filters to remove airborne particles, regularly vacuuming and dusting surfaces to reduce allergen buildup, and keeping windows open for ventilation when weather permits. Additionally, avoiding smoking and limiting the use of harsh chemicals and fragrances in the bedroom can help minimize indoor air pollution and promote better sleep.