When most people think about air pollution, they usually imagine smog, car emission, factory smoke, and the like.
However, these are all examples of outdoor air pollution. You may think you are safe from such pollutants inside your home, but this is far from the truth.
Indoor air pollution is more dangerous than outdoor kind. Therefore, it’s essential to understand what it is and how it comes about. From there, you can start making an effort to combat this danger.
Table of Contents
Defining Indoor Air Pollution
Air pollution is comprised of many elements. Many people may think that the major culprits are smog, car emissions, factory smoke, etc. They won’t be wrong, but these aren’t the only major contributors to air pollution.
They might not even be the most dangerous ones. However, things get dire when these elements enter the home and combine with indoor pollutants. This pollution is what we call indoor air pollution.
Indoor air pollution occurs when indoor areas are affected by poisonous gases, chemicals, and other dangerous substances. Since these elements are within a smaller space than the open outside, indoor air pollution could be more detrimental to health.
The result could be increased respiratory diseases like asthma or even fatal ones like cancer.
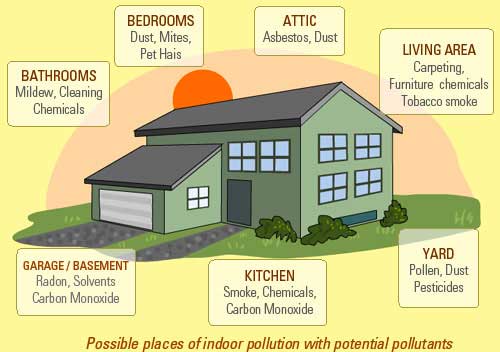
Causes of Indoor Air Pollution
The causes of indoor air pollution are many and varied. Some may even depend on where you live, your household products, and even how you cook at home.
The pollution level would also be affected by the absence or presence of good airflow, proper ventilation, and the building’s age.
Here are just a few causes of air pollution in offices, homes, and several other indoor spaces:
Preparing Meals
While air fryers and sous vide ovens are gaining more popularity, many people still stick to the pots and pans to get their cooking done. This could include using gas, wood, coal, charcoal, dung, or other waste.
Even if you use electric cooking methods, the temperature in your building will rise due to this activity. If not properly handled, the heat could increase air pollutants, toxins, and house pollution.
Concentration of Pollutants
The number of pollutants in the house may not be higher than the outside, but the air pollution inside is in a much smaller space, which could easily harm any person within the building’s boundaries.
Thus, it’s no surprise that indoor air pollution is responsible for a whopping 2 million deaths yearly.
Asbestos
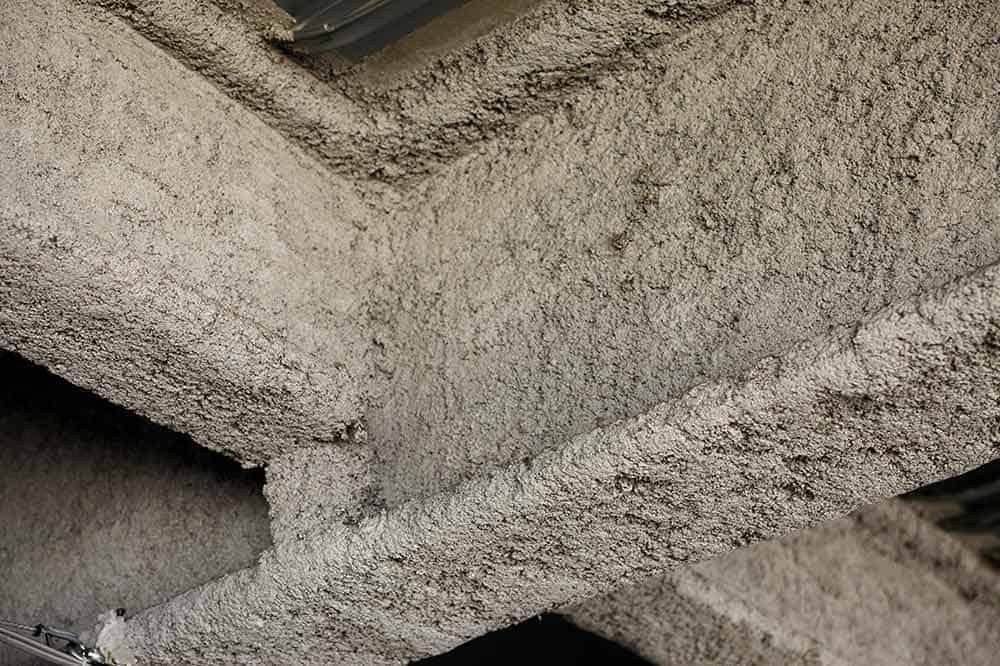

This is believed to be the main cause of indoor air pollution. It’s found in several materials, especially those commonly utilized by the automotive industry.
The home construction industry is related to this so you might find asbestos in your ceiling tiles, floor tiles, building material, paints, and coatings.
However, the newer materials usually don’t have asbestos, so you should only check for this particular trigger if your house or workplace is relatively old.
Asbestos can lead to lung and several other kinds of cancer, asbestosis, and mesothelioma. These diseases could be life-threatening, so take the appropriate steps if you discover asbestos in your home.
Formaldehyde
Formaldehyde is another major cause that must be controlled as soon as possible. It may have been officially banned in the US since 1970 but may still turn up in wooden flooring, paints, and sealants.
Radon
This harmful substance is usually found in homes with bedrock or similar materials. It can seep into the walls and provide an excellent risk for those living within them. More about radon here.
Tobacco Smoke
There’s a reason why many smokers are told to smoke outside the house. Having tobacco smoke permeates the walls of a house or office building can pollute the indoor air in a much more lasting manner than if the smoke was blown outside.
Contaminants from Damp Environments
Like mildew, mold, and fungus, several types of contaminants grow outside in a damp environment. If you are not careful, their spores could come floating inside and make a home within your home. These could also include animal dander, dust mites, and bacteria.
All of these combined would raise the risk of allergies, even if you don’t go outside. These usually include irritation in the throat, influenza, and several kinds of infections.
Heat Sources
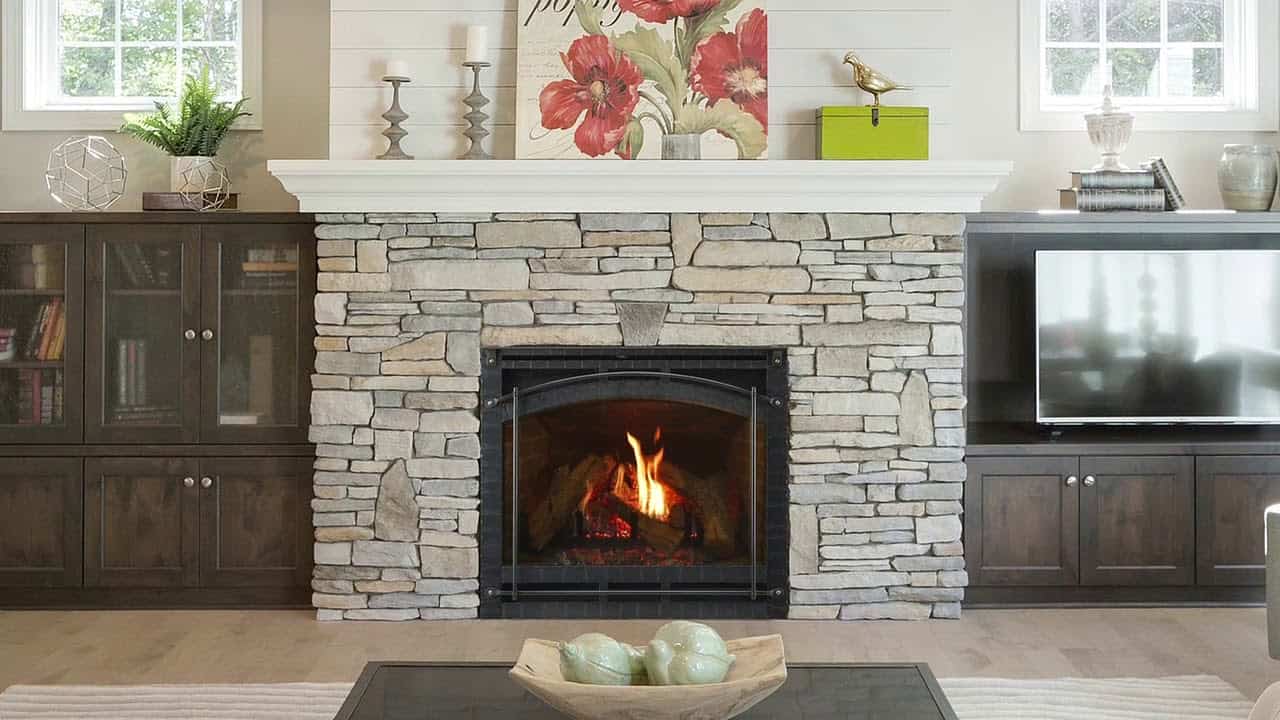

Apart from stoves and appliances, there are several other places where your house could be heated to a dangerous level. These would include space heaters, fireplaces, and even gas heaters if you have them.
The result would be an emission of carbon monoxide and nitrogen dioxide. Many still use such sources to heat their houses or rooms. When used daily, these sources would increase indoor air pollution by a large amount.
Lead
Lead is a poisonous substance but, unfortunately, one that’s commonly used in old houses. There may even be lead paint in the house, leading to lead poisoning if consumed by children. Even if no one ingests the substance, they could get seriously sick by inhaling its odor.
If lead poisoning takes place, the results could be highly severe. These include anemia, cardiovascular system problems, kidney failure, nerve damage, and brain damage.
Household Products
Many homeowners use varnishes, cleaning products, and paints that emit smells and chemicals into the air. If the area treated with such chemicals is not adequately ventilated, the indoor air pollution will reach new heights.
Conclusion
The steps toward combating indoor air pollution may be relatively new and unfamiliar.
However, it is hoped that this technology will become more common and inexpensive as time passes. We can only make efforts to leave a cleaner future for our future generations, both inside and out.